The Novel Tank Diving assay (also known as the Novel Tank Test, NTT) uses vertical distribution in a novel environment as a validated measure of 'anxiety-like' behaviours in adult zebrafish.
Conceptually similar to the rodent open-field and elevated plus maze tasks, the novel tank diving test utilises zebrafish’s instinctive behaviour to seek protection in novel environments. When first introduced to a novel tank, zebrafish will dive to the bottom and gradually increase their vertical swimming over time. This gradual increase in exploration is interpreted as a reduction in anxiety.
The novel tank diving test is quick to implement (5-10 minutes) and sensitive to various pharmacological, genetic, and environmental manipulations.
There are a number of options for performing the novel tank diving assay in the Zantiks systems. Here we will present a 2D tank diving assay in the AD, a higher throughput 2D tank diving assay in the LT, and a 3D novel tank diving assay in the LT system. If you need support with a different set up for a novel tank diving assay, please contact us.
Two zebrafish in a Novel tank diving test in the Zantiks LT.
A single zebrafish in a Novel tank diving test in the Zantiks AD. Courtesy of Dr Matt Parker's lab, University of Portsmouth
Experimental set up in the Zantiks AD
The Zantiks AD unit comes supplied with a novel tank diving kit, which includes a tank, a funnel, a tank stand, two stand locator strips, and a foam door.
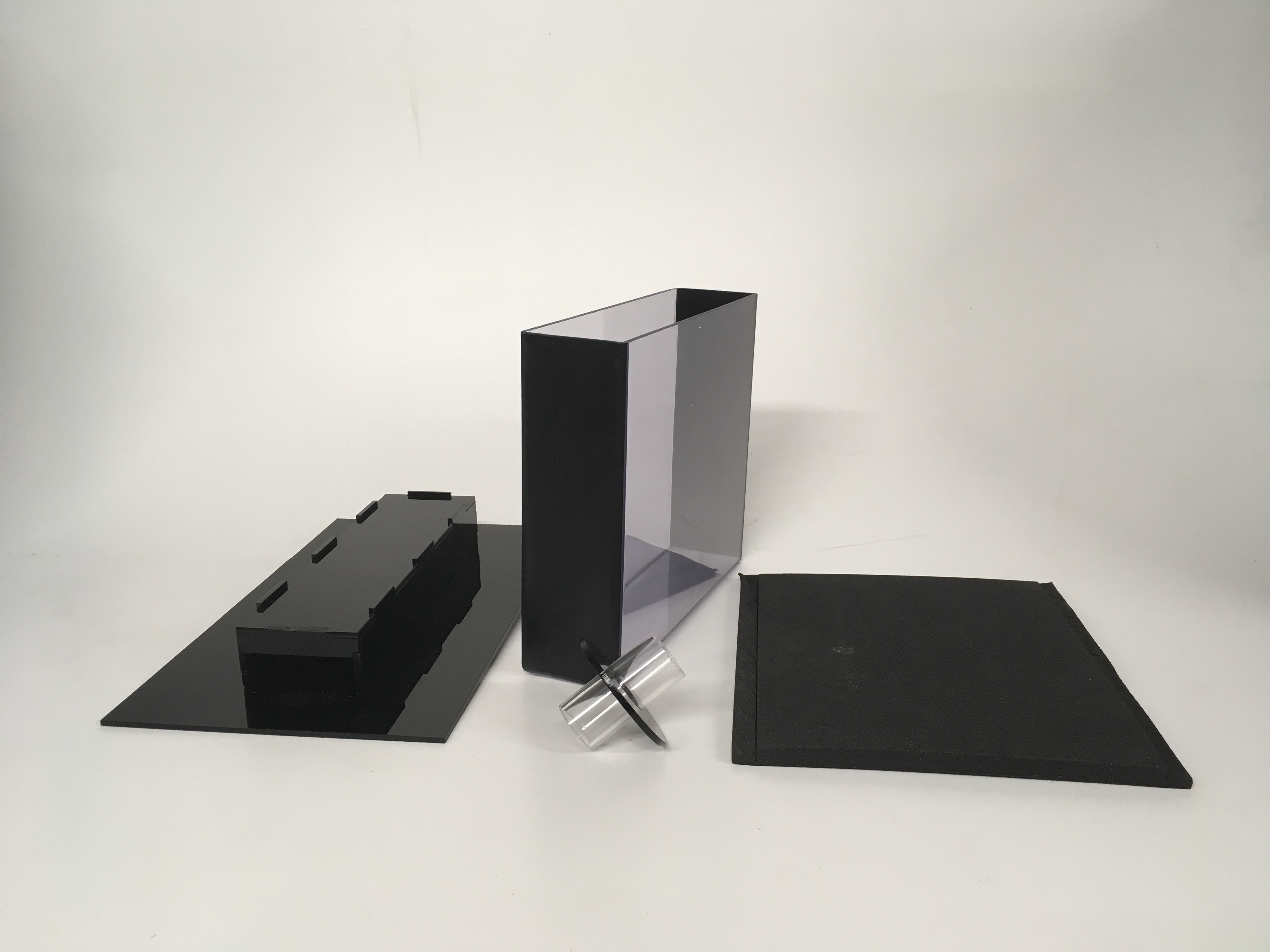 Novel tank diving insert kit for AD includes a tank, a stand, a fish funnel and a foam door.
Novel tank diving insert kit for AD includes a tank, a stand, a fish funnel and a foam door.
To conduct the novel tank diving assay in the Zantiks AD unit:
- Place the entire system on its side, with the covered hole facing up.
- With the AD unit placed on its side, the tracking camera will now have a side view of the fish’s movements in the testing tank.
- The ‘floor screen’ is now located behind the novel testing tank and will be used for illumination from the back of the tank.
- The LED ‘ceiling lights’ are now located in front the tank and can be used to illuminate the tank from the front.
- Insert the funnel into the hole on the unit’s side, turning it slightly to help ease it in.
- The tank stand should be placed into the centre of the chamber opening with the locator strips on either side to secure it in place.
- NOTE: Make sure that the ridge on the stand’s raised platform is situated at the back of the unit, so that the tank can slide in easily.
- After filling the tank with water, slide it onto the stand, ensuring that it is secure on the raised platform.
- Insert the foam door to isolate the testing chamber.
Seting up the Zantiks AD unit for a novel tank diving assay with zebrafish
Experimental set up in the Zantiks LT - 2D
SideView Stand
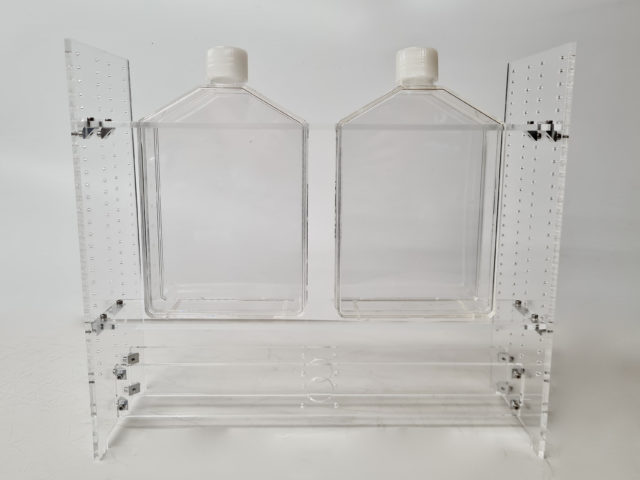
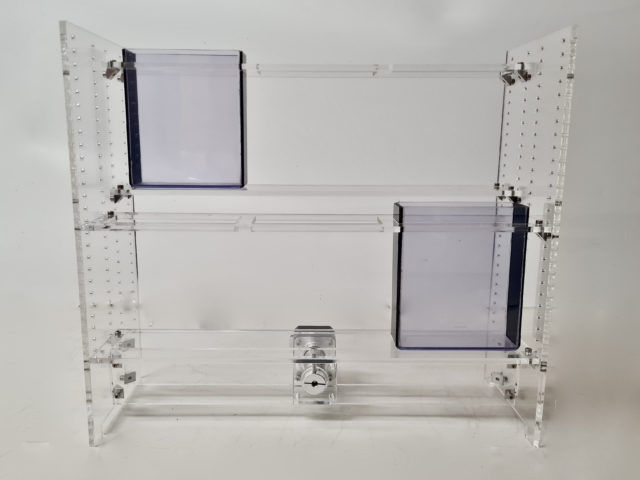
The optional SideView Stand add on can be used to conduct the Novel Tank Diving assay in the Zantiks LT. The stand can be configured to hold two T-225 cell culture flasks (max. 370 mL), three T-150 flasks, 6 T-75 flasks, or 6 black-sided tanks, allowing two, three or six adult zebrafish to be tracked at once. Information on how to assemble the side view stand can be found in the LT manual.
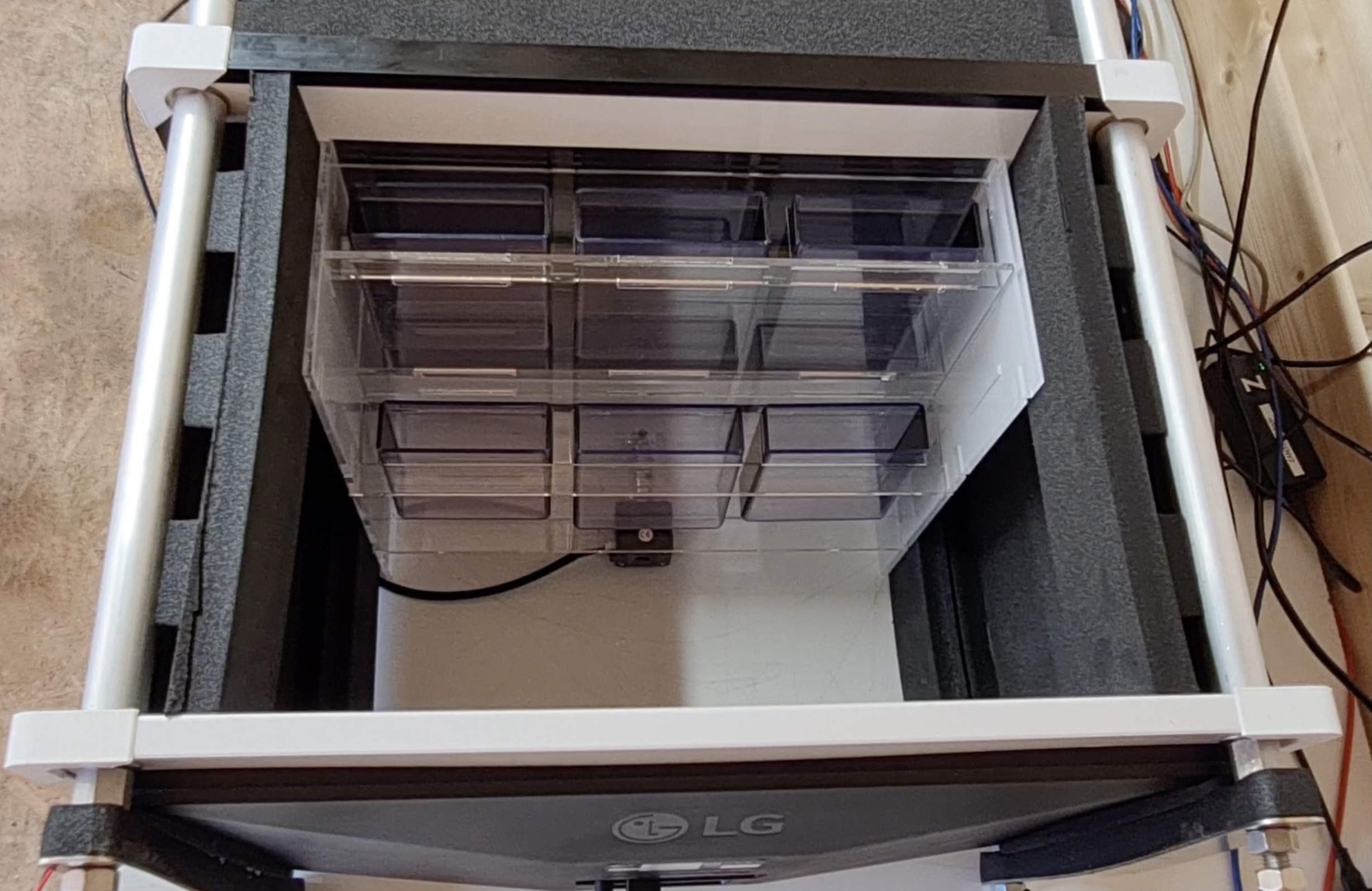



A detailed guide to setting up the side stand inside the Zantiks LT unit including step-by-step video can be found in the LT manual.
To conduct the novel tank diving assay in the Zantiks LT unit with the SideView Stand:
- Remove the front and rear foam panels and place the entire system on its side.
- With the LT unit placed on its side, the tracking camera will now have a side view of the fish’s movements in the testing tank(s).
- The ‘floor screen’ is now located behind the novel testing tank and will be used for illumination from the back of the tank.
- The LED ‘ceiling lights’ are now located in front the tank and can be used to illuminate the tank from the front.
- Place 2 of the locator foam strips at the bottom on either side of the chamber opening.
- These will act as a locator for standard positioning.
- Slide the stand into the unit so that it positioned against the middle layer of the LT (towards what was the 'top' of the system).
- Insert the last 2 locator foam strips flush with the top edge of the chamber opening.
- Fill the flasks, or tanks, with water and then place them into the SideView stand.
- Place the foam door on the top of the stand and unit to isolate the testing chamber.
Experimental set up in the Zantiks LT - 3D
3D tracking add-on
The 3D tracking unit optional add-on can also be used to conduct the Novel Tank Diving assay in the Zantiks LT. The 3D tracking unit is used with the 129 x 360mm sized LT tank, allowing X,Y and Z coordinates to be collected simultaneously without the need of an additional camera. Information on how to set up the 3D tracking unit in the LT can be found in the LT manual.
3D tracking of an adult zebrafish in a novel tank dive assay
Experimental procedure
Fish should be singly housed for one week prior to behavioural testing. If not already housed in the experimental room, allow one hour to for the fish to acclimatise to the experimental room. The novel tank should be filled with water up to 13cm deep (in the case of the 3D setup, the water should be filled to the level that reaches the top of the mirror box). Fish are tested individually in the novel tank.
If running the experiment in the AD system the experiment can be started via the console before the fish is placed in the tank. Recording will begin immediately after the fish enters the experimental arena. Introduce the fish into the tank by netting it through the funnel at the top. When using multiple tanks in the LT system or for the 3D setup, fish should be introduced to the tank and then the experiment can be started via the console once all fish at in the tanks of the side view stand or after the IR light has been attached for the 3D setup.
Each trial will last 5-10 minutes. All fish can only experience the novel tank once.
Results / data ouput
For analysis, the tank is virtually divided into 2 (top, bottom) or 3 (top, middle, bottom) equally target zones. The relative position in the zones is taken as the index of anxiety. Time spent and distance travelled in each zone, as well as entries into the zones can all be recorded automatically by the Zantiks AD unit.
Common variables measured in a novel tank diving assay include:
- Latency to enter the top (s): amount of time it takes the fish to enter into the top zone of the tank - main measure of anxiety level. The longer the fish takes to enter the top zone, the higher the anxiety level is interpreted to be.
- Time spent in zones (s): total time spent in each zone - a longer duration in the top of the tank indicates lower anxiety levels.
- Number of entries to the top: number of entries into the top zone - more top entries indicates lower anxiety levels.
- Distance travelled in the top (mm): total distance travelled in the top zone - more distance travelled in the bottom of the tank indicates higher anxiety levels.
- Total distance travelled (mm): total distance the fish has travelled throughout the entire novel tank - can reflect general motor/neurological phenotypes.
- Average entry duration (s): average time spent at the top of the tank following an entry. Calculated as time spent in the top / number of entries into the top. Shorter average entry duration indicates higher anxiety level.
Protocol scripts download
There is one script for the Novel Tank Diving Task for adult zebrafish.
There are two assets that can be use for the novel tank diving assay. You can choose to 'divide' the tank into two target zones: the 'bottom' and 'top' of the tank or three target zones: the 'bottom', 'middle' and 'top' of the tank. There are different assets required for the Zantiks AD, the Zantiks LT 2D and 3D setups.
For a single tank with a 2D side view in the AD system split into three zones use the demo script:
For the 3D setup in the LT system and the side view split into three zones use the demo script:
To edit this script for other novel tank setups you will only need to change the asset that is loaded plus the headings of the data output to match the correct number of zones. Contact us if you need help adapting your script to your experimental needs.
Assets
You will need to upload the appropriate asset into the Asset directory on your Zantiks Control Console and ensure the correct asset name is in the LOAD(ZONES,"name_of_asset") command in the script.
See the Calibrating your Zantiks unit page and Asset building in the AD unit page or Asset building in the LT unit page for details on how to create assets customised to your system.



