CPP is a form of Pavlovian conditioning that is used to investigate the rewarding effects associated with drugs of abuse.
Adult zebrafish are conditioned to associate drug exposure with specific (neutral) environmental stimuli. The aim of this experiment is to measure the amount of time spent in a particular environment that has previously been associated with a substance (drug), indicating positive-reinforcing qualities of that compound.
Experimental setup
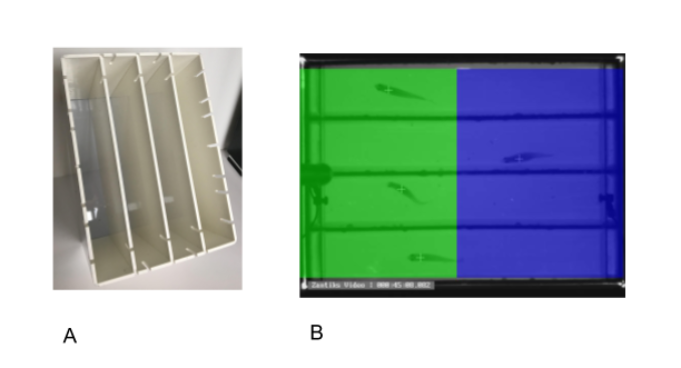
The Zantiks AD and LT units can be used for CPP in zebrafish. The dividing inserts are used to create four separate testing compartments for tracking four fish in one unit (see image A above). Stimuli are presented from the integrated screen below the testing tank. The stimuli can be comprised of colour, shapes, or stripes and be both biased and unbiased in presentation (see image B).
Experimental procedure
The CPP paradigm is conducted in three testing phases occurring on consecutive days.
- *IMPORTANT Single housing: In order to reduce any stress effects, the fish to be tested should be singly housed for one week prior to a habituation phase.
- Habituation/Autoshaping: For two days before recording CPP, individual fish should also be gently netted and placed in tank and allowed to swim freely for 10-20 minutes. This step allows the fish to habituate to the new testing environment.
- Baseline: In the first testing phase, baseline preferences for two distinct environments are recorded. Fish are placed into individual arenas for a 20 minute period, during which, each fish is allowed to explore its full arena with both stimuli shown together. The Zantiks units can automatically track and measure the time spent and distances travelled within the two stimuli environments to calculate a baseline preference.
- Calculation of the percentage and baseline stimulus preference. The proportion of time spent in the vicinity of each of the stimuli for baseline is calculated as: Time in Stimulus A / (Time in Stimulus A + Time in Stimulus B).
- Conditioning: Following establishment of baseline preferences, on three consecutive days, the fish are exposed to the test compound or control treatment in the presence of the least-preferred stimulus (stimulus in which the fish spent the least amount of time during baseline). Fish are placed into arenas individually, with the preferred stimulus (stimulus in which the fish spent the most time during baseline) projected for 20 minutes. The stimulus is then changed to the least-preferred stimulus for 20 minutes and the test compound or saline is administered into the tank.
- Fish are returned to home tank, and testing tank is washed out.
- Probe: After the 3 days of conditioning, any change in preference is determined using a probe trial. This step is identical to the baseline recordings. Fish are placed into the tank for a 20 minute period. Both stimuli are presented together, and the fish has free range of the arena. The amount of time and distance travelled within either stimulus environment is measured.
- Calculation of the percentage and probe stimulus preference. Change in place preference (CPP Change Score) is calculated by subtracting the percentage of time spent in the drug-paired environment before conditioning from the percentage of time in the drug-paired environment after conditioning, and expressed as a percentage.
Results / Data output
The behavioural endpoints typically measured in this task include distance travelled in each stimulus zone, time spent in each stimulus zone, number of entries into each zone, and total distance travelled. The Zantiks units can automatically measure and process these behavioural endpoints in an easy to read format.
An increase in time spent in the drug-paired environment relative to a control is taken as evidence that the test compound was rewarding (calculated as the CPP Change Score). The learned association between the environmental stimulus and the test compound results in the fish spending more time in that environmental stimulus.
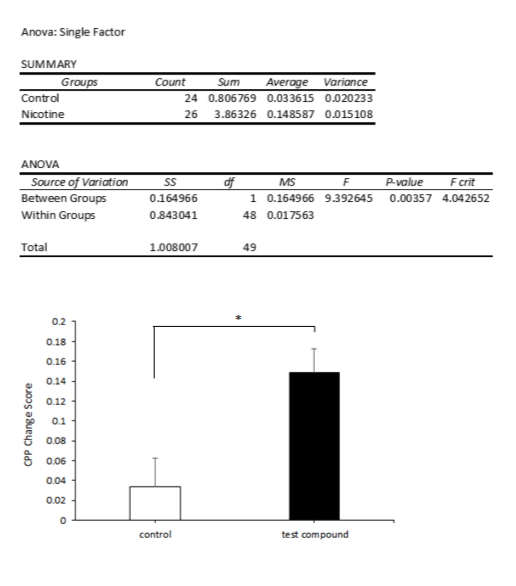
CPP change scores are frequently analysed by a one-way ANOVA comparing doses of treatment conditions.
Typical findings when a significant change in preference towards the drug-paired environment is observed, revealing an established conditioned place preference.
Protocol scripts downloads
There are two scripts for the Conditioned Place Preference for adult zebrafish: a baseline/probe script and a drug treatment script.
There are two assets you will use. The zones asset will 'divide' your testing tank in two separate target zones where your stimuli will be presented. The arena asset will 'divide' the testing tank into two arenas: one for each individual fish.
Assets
You will need to upload the appropriate asset into the Asset directory on your Zantiks Control Console and ensure the correct asset name is in the LOAD(ZONES,"name_of_asset") and the LOAD(ARENAS,"name_of_asset") commands in the script.
See the Calibrating your Zantiks unit page and Asset building in the AD unit page or Asset building in the LT unit page for details on how to create assets customised to your system.
NOTE: The typical assets used for the CPP task is an "arena asset" with 2 separate swimming lanes oriented across the length of the tank and a "zone asset" with 2 tracking areas across the width of those 2 swimming lanes.
Sprite images
When using sprite images for your stimuli, you will also need to upload them into the Assets directory and include them in the script. The following images are a checked pattern vs a grey colour.



